PRTG Manual: REST JSON Data Sensor
The REST JSON Data sensor accesses a Representational State Transfer (REST) application programming interface (API) endpoint and retrieves JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) encoded data.
This sensor is in beta status. The operating methods and the available settings are still subject to change. Do not expect that all functions work properly, or that this sensor works as expected at all.
For a detailed list and descriptions of the channels that this sensor can show, see section Channel List.
- Dutch: REST JSON Data
- French: REST JSON Data
- German: REST JSON Daten
- Japanese: REST JSON Data
- Portuguese: REST JSON Data
- Russian: REST JSON Data
- Simplified Chinese: REST JSON Data
- Spanish: Datos REST JSON
Consider the following remarks and requirements for this sensor:
Requirement |
Description |
|---|---|
This sensor requires that the Beta Sensors experimental feature is enabled.
|
|
Credentials |
This sensor requires credentials for REST API in settings that are higher in the object hierarchy. |
JSON Schema |
For more information about the JSON schema that this sensor uses, see the Knowledge Base: Where can I find the JSON schema against which a sensor validates my script output? |
IPv6 |
This sensor supports IPv6. |
Smart URL replacement |
This sensor supports smart URL replacement. |
Channels |
This sensor does not officially support more than 50 channels. |
Performance impact |
This sensor has a very low performance impact. |
Lookups |
This sensor uses lookups to determine the status values of one or more channels. |
Scanning interval |
This sensor has a fixed minimum scanning interval for performance reasons. You cannot use a shorter scanning interval. Consequently, shorter scanning intervals in the Monitoring settings are not available for this sensor.
|
Multi-platform probe |
You can add this sensor to a multi-platform probe. |
The sensor has the following default tags that are automatically predefined in the sensor's settings when you add the sensor:
- rest
For more information about basic sensor settings, see section Sensor Settings.
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
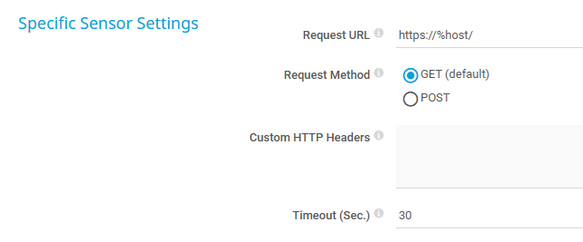
Request URL |
Enter the URL that you want to request. This setting supports smart URL replacement. If you enter http:///, PRTG automatically fills in the IP address or DNS name of the parent device. The default URL is https://%host/.
|
Request Method |
Select the HTTP request method that the sensor uses to request the REST API:
|
POST Body |
This setting is only visible if you select POST above. Enter the data part for the POST request.
|
Custom HTTP Headers |
Enter custom HTTP headers that the REST API request of the sensor contains. Each line must contain a valid HTTP header like key:value.
|
Timeout (Sec.) |
Enter a timeout in seconds for the request. Enter an integer. The maximum timeout value is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Primary Channel |
Select a channel from the list to define it as the primary channel. In the device tree, PRTG displays the last value of the primary channel below the sensor's name. The available options depend on what channels are available for this sensor.
|
Graph Type |
Define how this sensor shows different channels:
|
Stack Unit |
This setting is only visible if you select Stack channels on top of each other above. Select a unit from the list. PRTG stacks all channels with this unit on top of each other. By default, you cannot exclude single channels from stacking if they use the selected unit. However, there is an advanced procedure to do so. |
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Result Handling |
Define what PRTG does with the sensor result:
|
By default, all of these settings are inherited from objects that are higher in the hierarchy. We recommend that you change them centrally in the root group settings if necessary. To change a setting for this object only, click ![]() under the corresponding setting name to disable the inheritance and to display its options.
under the corresponding setting name to disable the inheritance and to display its options.
For more information, see section Inheritance of Settings.
- Instead of entering a complete address in the Request URL corresponding field of the sensor, you can also enter the protocol followed by a colon and three forward slashes (this means that you can enter either http:/// or https:///, or even a simple forward slash / as the equivalent for http:///). PRTG automatically fills in the parent device's IP Address/DNS Name in front of the third forward slash.
- Whether this results in a valid URL or not depends on the IP address or Domain Name System (DNS) name of the parent device. In combination with cloning devices, you can use smart URL replacement to create many similar devices.
For example, if you create a device with the DNS name www.example.com and you add the sensor to it, you can provide values in the following ways:
- If you enter https:/// in the Request URL field, PRTG automatically creates the URL https://www.example.com/.
- If you enter /help in the Request URL field, PRTG automatically creates the URL https://www.example.com/help.
- It is also possible to provide a port number in the Request URL field. It is taken over by the device's DNS name and is internally added, for example, https://:1616/.
Smart URL replacement does not work for sensors that run on the probe device.
Which channels the sensor actually shows might depend on the target device, the available components, and the sensor setup.
Channel |
Description |
|---|---|
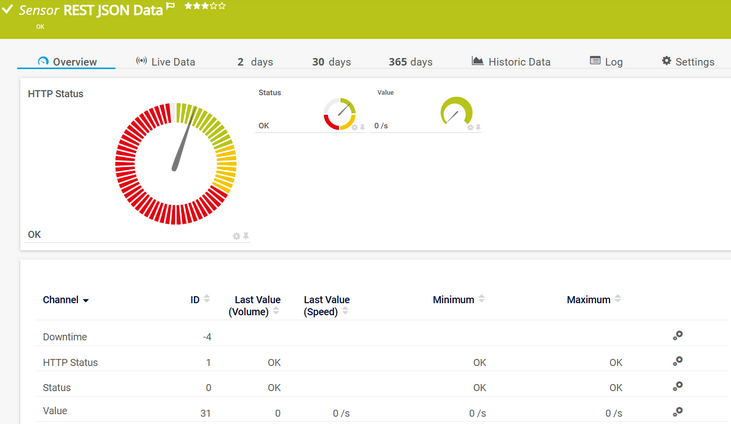
Downtime |
In the channel table on the Overview tab, this channel never shows any values. PRTG uses this channel in graphs and reports to show the amount of time in which the sensor was in the Down status. |
HTTP Status |
The HTTP status that the requested URL returns
|
Status |
The status of the given endpoint
|
[Value] |
The values that a REST API returns in several channels |
KNOWLEDGE BASE
What are beta sensors and how can I use them?
What security features does PRTG include?
Where can I find the JSON schema against which a sensor validates my script output?